
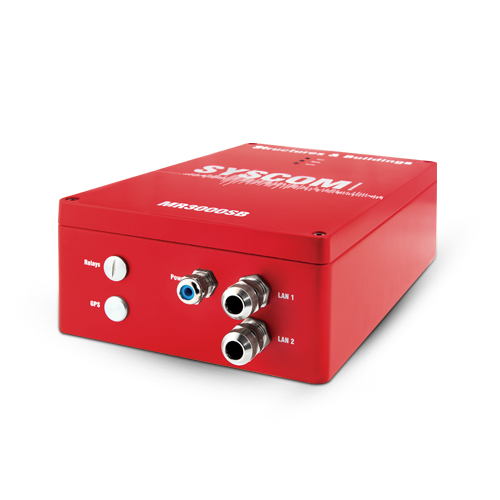
Building monitoring: MR3000SB
The vibration monitoring in buildings is very important in order to control the structure integrity, to increase the human safety and to evaluate the human disturbance. It is also fundamental in case of new construction sites and in case of high seismic zones.
The vibration monitoring can give important information about risk assessment of a building, both in direct terms (acceleration/velocity) and indirect terms (frequency, post-processing analyses), as well as information about the accuracy of a structure’s development, right from the start.
We can integrate the building monitoring system with building management system solutions (BMS), that contribute to the automation, activation and controlling of multiple parametres (for example: temperature, humidity, closed/ open, active/ innactive and so on) in any given risk situations.

The most important applications
- Strong-motion monitoring
It is dedicated to buildings in high seismic zones, as defined by local or national geophysical institutes. The standard configuration includes 4 tri-axial accelerometers, one in the free field to properly record the earthquake and three inside the buildings (foundation, middle and top). The units are typically placed on the ground, close to the load-bearing walls of the structure.
- Structural damage
The analyses according to the structural damage norms are needed for buildings around a construction site. The typical configuration is with 3 tri-axial sensors (accelerometers or geophones) inside the building, close to the load-bearing walls. The most important features are the velocity peaks and maximum frequencies, calculated according to the main international standards, such as DIN 4150-3 and SN 640312.
- Human comfort
The analyses related to the human comfort evaluation are usually connected to structural damage measurements or noise measurements. Typically, a tri-axial sensor (accelerometer or geophone) is placed inside the building, in a place particularly sensitive for the people disturbance, like the bedroom for example. The most important standards are DIN 4150-2 and ISO 2631.
- Modal analysis
The modal analysis is a collection of algorithms and techniques for the characterization of the structures, by obtaining natural frequencies, damping factors and mode shapes. It is mainly required for the design and testing of newly built structures to prevent resonance conditions. Depending on the structure, the number and the typology of the accelerometers could be very different. In case of unknown excitation input, the procedure is called Operational Modal Analysis (OMA).
Main Benefits



Main Features
- IP67 compact unit containing tri-axial MEMS sensor, digital recorder, battery and communications
- No need of periodic calibration
- Digital interconnection through Fiber Optics or Ethernet copper type cable with minimal noise
- Common timing and common triggering
- Automatic alerting and self-test
- Remote control and data retrieval
Technical specifications
Data acquisition
- General principle 4th order delta-sigma ADC per channel
- Resolution 24 bits
- Sampling-rate 50, 100, 200, 400, 500, 800, 1000, 2000 sps
- Number of channels 3
- Channel to channel skew None, simultaneous sampling on all channels
- Data Filter Anti-aliasing filters
- Trigger Filter Digital IIR filter: 0.5 – 15 Hz band-pass (Strong Motion Applications)
Data acquisition
- General principle 4th order delta-sigma ADC per channel
- Resolution 24 bits
- Sampling-rate 50, 100, 200, 400, 500, 800, 1000, 2000 sps
- Number of channels 3
- Channel to channel skew None, simultaneous sampling on all channels
- Data Filter Anti-aliasing filters
- Trigger Filter Digital IIR filter: 0.5 – 15 Hz band-pass (Strong Motion Applications)
Trigger and de-trigger
- Principle Level trigger or STA/LTA or automatic adjustment of trigger level
- Trigger voting logic Predefined AND or OR combinations, individual channel votes
- Trigger level 1 mg to 4 g
- STA / LTA STA: 0.1 to 25s, LTA: 1 to 250s, ratio 0.1:25
- Smart Trigger / De-Trigger Automatic adjustment of trigger level
Microprocessor
- Recording
- Principle Event recording (time history), continuous time recording or manually triggered
- Header Contains status information at time of trigger and event summary
- Pre-event recording 1-30 s (in 1 second steps)
- Post-event recording 1-100 s (in 1 second steps)
- recording time Unlimited
- Memory Removable SD flash card (4GB)
- Timing
- System clock 1ppm, could be disciplined by NTP or GPS (optional)
- Data / User Interface
- Web interface Easy to use command & control through embedded web server
- Intelligent Alerting System initiates communications and sends e-mail when an event is recorded
- FTP Built-in FTP client to push data to an FTP-server
- API Application programming interface REST with extended functions available
- Alarm triggers
- Principle Two alarm levels independently settable as threshold levels or user-defined curves, with various notification options (individually settable for each axis)
- Alarm level range 1 % to 100% full scale
- User-defined alarm Thresholds and frequencies individually settable for each axis
- System status 3 LEDs Run, Recording, Warning/Error. Internal LCD with status info and important settings
Network capabilities
- Common trigger and Configurable with AND/OR logic, for every device within the same network common alarm
- in LAN network Typically 1 ms with NTP protocol
- number of MR3000SB 32, in Master/Slave configuration
- Remote control VPN, DDNS
Power Supply
- Power supply 100 – 240 V AC, 50 – 60 Hz, internal AC/DC. Optional DC power 10-36 V DC
- Internal battery 12 V, 12 Ah
- Consumption 4 W (with charged battery), 25 W (AC max. and battery in charge)
- Battery autonomy Typical 60 hours in stand-alone mode
I/O (glands and connectors)
- Power M16 cable gland 4-11mm / Terminals on the AC/DC
- Kit Relays (3) On request, M16 cable gland 7-11mm / Terminals
- Kit daisy-chain LAN On request, RJ45 panel mount
- Kit daisy-chain FO On request, M20 cable gland 6-13mm / ST connectors
- Kit GPS On request, connector and GPS antenna with 5 m cable for time synchronization
LAN cables
- Fiber Optic type Multimode OM2 fiber with wavelength 1300 nm, 50/125 μm, Rx/Tx
- Ethernet Copper type Cat 5e, <100m
Relays kit
- Configuration 3 output configurable relays, No/Nc
- Current 2 A, 30 V DC
Acceleration sensor
- Principle Micro-machined capacity MEMS accelerometer
- Hysteresis None
- Noise (10 to 1000 Hz) 7 μg/√ Hz
- Frequency range DC to 600 Hz
- Dynamic range 100 dB @ 200 sps
- Measuring range ±4 g
- Sensitivity 25 V/g differential
- Scale factor error < 1 %
- Orientation Horizontal or vertical mounting, to be specified when ordering
- Self test Test-pulse, configurable
Housing
- Dimensions 330 x 230 x 110 mm
- Weight 5 Kg
- Protection degree IP67, temporary static immersion in water
Environmental
- Shock 30 g/11 ms half-sine
- Heat -20 °C to +50°C
- Humidity up to 100% RH
Regulations
- EMC IEC 61326-1
- Electrical safety IEC 61010
- Origin Swiss Made

For projects associated with other types of structures:
SHORT-TERM MONITORING

CONSTRUCTION SITE

STRUCTURAL HEALTH

BLASTING